Elena used to dream that one day she would head her own marketing agency.
But then the COVID-19 pandemic slashed the company’s revenues and transformed her job into something completely different. Since May this year, she has been reassigned to translating stories from English and Serbian media into Macedonian, and from Serbian into English, adjusting the content to create short, sensationalist articles with headlines that will catch a reader’s eye imediately – clickbait.
“I used to dream of one day creating a campaign for [US fashion designer] Marc Jacobs, now I just translate articles from dawn until dusk,” said Elena. “My boss lady says it’s the same thing, it’s just being a content writer – but is it?”
COVID-19 conspiracies shared on a website named Torix.info that publishes in the Croatian language. The website is part of the interests Aleksandar Filipovski shared on his Facebook page along with other similar websites, such as the currently inactive, German-language Newcome.net and the Serbian language BalkanEkspres.com. Screenshot: Saska Cvetkovska
The articles that are created at the marketing agency where Elena works end up being published on various websites with the aim of generating revenue from Google Ads, as well as being posted to a range of Facebook groups to drive click-throughs. BIRN is not naming the company in order to protect the anonymity of Elena, which is not her real name.
Elena showed BIRN her corporate and private emails dating from May 21 to October 2.
“Just take a look at one day in the office. Total brainwashing bullshit,” she said as she showed hundreds of emails sent to the 18 employees who survived staff cutbacks in July and have now been reassigned to work on the clickbait content, which they call “the dirty laundry”.
Asked to explain why they call it that, Elena responded sharply: “As a professional I find there are no ethics in what we are doing. No professional challenge, nor any excitement. I just need the job desperately,” she said.
“As a feminist and bisexual, I do not feel comfortable creating clickbait posts for articles like ‘You have no idea what she did to her boyfriend when she found out he was gay. Now he is paying the price before God,’” she explained.
She said the agency’s staff were shocked that the company’s director was willing to get involved in clickbait publishing. They have never told been the identity of the client or clients who are paying for the stories they produce, and the exact relationship between the agency and the websites that publish the articles is unclear.
According to Elena, the director simply told them: “For now, we will have to adapt. This what makes money, I didn’t invent it, but there are people with huge businesses that work exclusively with Google ads. This is the reality now.”
Back in 2016, world media reported how more than 100 websites had been set up in North Macedonia to target US readers ahead of that year’s presidential elections, most of them pumping out bogus stories aimed as boosting Donald Trump’s candidacy. Amazement was expressed at how young Macedonians, thousands of kilometres away from the US, were making money out of fake news about the American elections.
Four years later, some clickbait sites based in North Macedonia are still pumping out pro-Trump stories. But now entrepreneurs and companies with no political agenda have got involved, seeing an opportunity to earn easy money by mass-producing sensationalist content about the US elections and COVID-19 that will generate revenue from Google Ads.
BIRN spoke to four marketing agencies in North Macedonia that are now involved in creating clickbait content for international clients; two of them also create articles for domestic websites. With the country’s advertising and marketing business hit hard by the pandemic, they see it as one of the only ways to stay in business.
US elections change the agenda
 US President Donald J. Trump participates in a ‘Make America Great Again Victory Rally’ campaign event at the Richard B. Russell Airport in Rome, Georgia, USA, 2020. Photo: EPA-EFE/BRANDEN CAMP
US President Donald J. Trump participates in a ‘Make America Great Again Victory Rally’ campaign event at the Richard B. Russell Airport in Rome, Georgia, USA, 2020. Photo: EPA-EFE/BRANDEN CAMP
Around 60 per cent of the content created by the agency where Elena works was clickbait material about COVID-19 – emotional stories about survivors, poignant statements from doctors in hospitals, what world leaders have said on social media, what celebrities do or don’t do to protect themselves from the coronavirus, plus conspiracy theories and articles about famous people who think that COVID-19 doesn’t exist. Other topics included politics, health and beauty.
The stories, mostly translated from Serbian or Croatian tabloids’ websites, were generally presented with misleading headlines written in capital letters: “This is how the client wants it, our boss just says,” Elena explained.
On September 6, an email from the director set out a new priority for the agency’s employees: the mass production of clickbait articles about Donald Trump.
“Guys, as you know the US elections are coming. We have follow the trends and increase advertisements on Google Ads. That is what everyone is reading now. Trump, Trump, Trump, just follow that and US domestic policy,” the email said.
On October 6, another email from the director on October 2: “Please follow Donald Trump’s Twitter, too. Especially now he has COVID-19. The client wants headlines adapted from the videos he shares. Try to get hold of tweets that are crazier, or the ones in which he mocks the liberals, i.e. his opponents,” it said.
Elena noted that the clients are not interested in having just any story on Trump, but prefer positive content. She and her co-workers were introduced to at least 20 Facebook groups with names like Trump for USA or Conservatives for Trump, which they were supposed to use as sources of content.
They were told they could use anything as source material for a clickbait article, even a meme. They were asked to deliver “at least 30 articles per day”, she said.
Elena said she saw at least five headlines she personally created were picked up by hundreds of other media outlets. She said she found the whole clickbait phenomenon disturbing.
“As a reader, I would not want the media and journalists to work like this,” she said. “As a marketing person, I never dreamed that we would do this. As a citizen, honestly, I find this a dangerous trend. This is becoming a big industry.”
Trump and the North Macedonian connection
The moto of TILT news is “conservatives uncensored”. Screenshot: Saska Cvetkovska
Among the suggestions that Elena and her colleagues were given for sources of content was a website named TiLT News, whose slogan is “Unfiltered Conservatism”. Her boss described it as a “great source, according to the client, aggregating the most important tweets and Facebook posts from US President Donald Trump”.
Some TiLT News headlines also took readers through to well-known US right-wing and pro-Trump sites like Breitbart News.
BIRN’s efforts to find out who is behind TiLT News led back to the notorious websites that operated out of the North Macedonian towns of Veles and Kumanovo during the 2016 US presidential elections, with the aim of affecting the outcome by targeting American readers with positive news about Trump and attacks on his opponent Hillary Clinton.
More than 100 websites with names like DonaldTrumpNews.co and USADailyPolitics.com were launched by a North Macedonian lawyer who was working with US conservative partners.
There is no data about the owner of TiLT News on the site due to protected anonymity, which can be bought for $15 a year from the Internet domain registrar and web hosting company GoDaddy. However, BIRN found that an email address that was used to register TiLT News, tamiterusa@hotmail.com, was also used to register some of the pro-Trump conservative clickbait websites in North Macedonia that were operating in 2016.
One of those involved was Aleksandar Filipovski, who in 2016 worked on producing pro-Trump articles on behalf of the US conservative lobby.
Links to Filipovski’s websites that were registered in 2015 and 2016 have since been removed from Facebook and Twitter. But his network of false Facebook accounts still exists, using PhotoShopped profile pictures that are hard to identify as modified fakes.
These fake accounts share TiLT News items to hundreds of US conservative groups’ Facebook pages, as well as to military veterans’ groups and other pro-Trump groups.
How the clickbait business works
In 2016, TiLT news published fake news claiming that former US President Barak Obama is an alien. At the time, the website was named the Tamiterusa blog. If you google TiLT news, you will only get results for Tamiterusa, most of which dates back to before the 2016 presidential elections. Screenshot: Saska Cvetkovska
To explain the clickbait business model, BIRN asked Aleksandar Velkovski, a 28-year-old bank official from Skopje who earns money on the side by running five different websites, three in English and two in Macedonian.
Velkovski said that after setting up their websites and paying the fee to keep their ownership anonymous, clickbait entrepreneurs need to acquire more than 30 fake Facebook profiles that they can use to promote their articles.
“Then [get the fake profiles to] join as many Facebook groups as possible because you’re not a real news brand, no one knows you and you just need the clicks so that Google Ads can work for you,” he said.
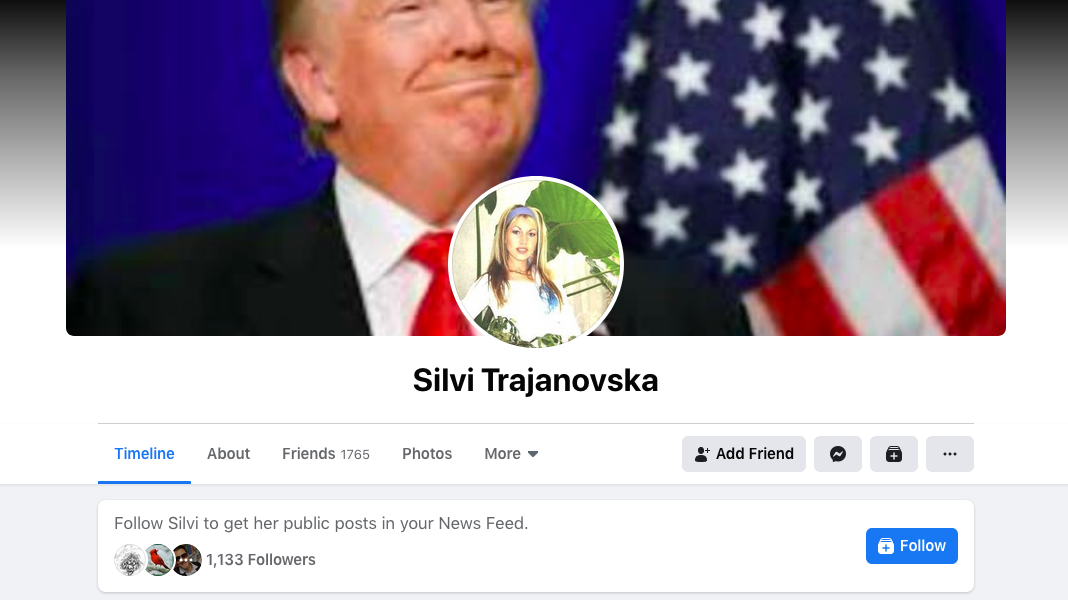
Silvi Trajanovska was an active profile in 2016. She has Macedonian friends, some of whom are fake profiles, but some are real. BIRN tracked her sharing and liking TiLT news, and became members in groups that share this and other conservative content but were not able to confirm whether this profile is real or not. Screenshot: Saska Cvetkovska
The fake profiles then post the clickbait articles in the Facebook groups. “From a group of 150,000 members, at least 30 per cent will click [on a clickbait link]. If the topic is currently ‘hot’, like the US elections or COVID, you can get around $100 to $300 out of one article from Google Ads,” he continued.
Velkovski doesn’t produce content himself, but orders it from various suppliers.
“I can pay a content provider for English news like $1,000 per month, and on top of that I have two more people from Skopje who I’m paying 400 euros each, and there is money left over for me as well. I’m not going to tell you exactly how much, but a bit more than double the costs.”
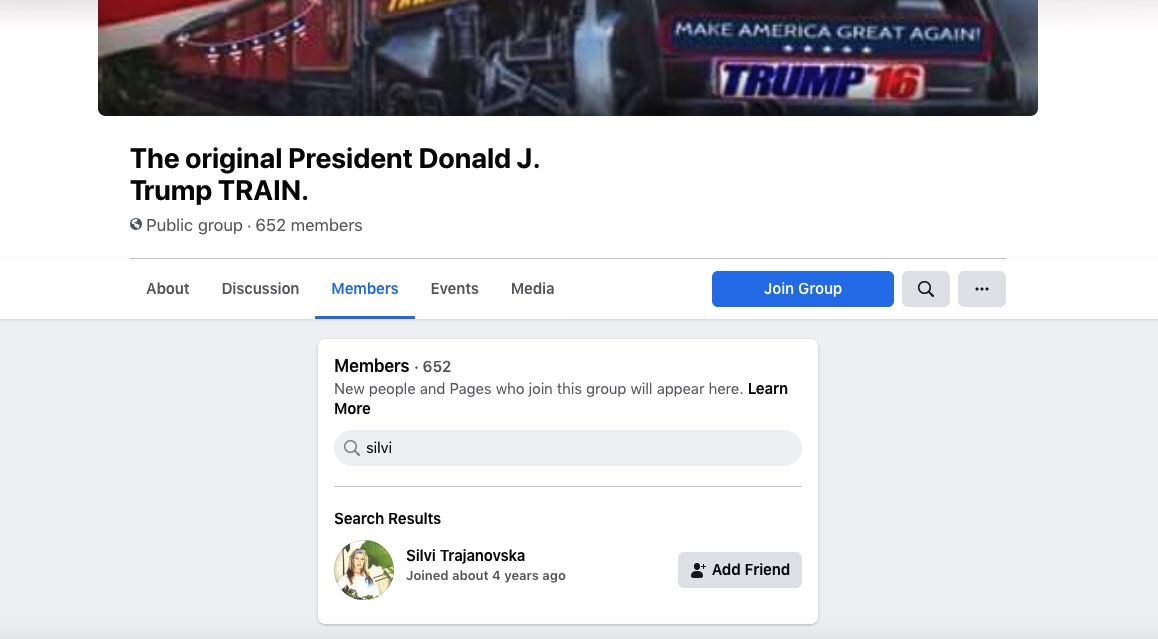
Silvi Trajanovska in one of the groups sharing TiLT news and other conservative news content. Screenshot: Saska Cvetkovska
Rosana Aleksovska, the director of F2N2, a fact-checking service that also investigates disinformation narratives, said that clickbait entrepreneurs are now not only promoting their sites using networks of fake profiles on Facebook and Twitter, but also now increasingly on Instagram and Telegram. “The bigger your social media platforms are, the bigger your earnings,” she said.
When it comes to disinformation campaigns, Aleksovska suggested that “most of this type of content is linked to conservative and extreme-right politics and opinions”. Some sites are ideologically-driven, some have murky connections to Russia. But other sites aren’t concerned about the politics of their content, she noted: “This is about money now, this has truly become a business.”
North Macedonia’s Media Ethics Council, an independent body, has been trying to address the issues of disinformation and political propaganda in media as well as pushing for transparency in media ownership. It runs the media transparency registry, where media ownership is listed, although disclosure is not compulsory under the law.
The council says it sometimes receives more than 100 complaints from the public each month.
“Most of the cases we receive are related to violations of Article 1 of the Code of Journalists, which refers to the publication of accurate and verified information, and in 39 per cent of reported cases this is the problem, while violations of Article 8 of the Code of Journalists, which refers to sensationalist information, were found in 35 per cent of the reported cases,” explained Katarina Sinadinovska, the president of the council.
‘Fake news’ and sensationalist stories are genuine worries for the public, Sinadinovska said: “You have a sea of unverified information, full of sensationalism, and we are not sure who makes the news anymore,” she pointed out.
Clickbait journalism as a career option

Illustration. Photo: Unsplash/Nick Morrison
Lila Karjlieva, a young Macedonian journalist, until recently worked for a website in the capital Skopje that pumps out clickbait articles. When she went for the interview, she was not expecting her first job in journalism to be the greatest in North Macedonia, but what she was told by her prospective employer surprised her.
“‘You’re young and there’s plenty of time for real journalism; this is content creation, a different kind of journalism’ – this is what Filip told me when I asked why we were working from home. You know, I was expecting a real newsroom,” Karjlieva recalled. “I had been following that website for about four years, and I thought real reporters worked there.”
The three owners of the site all have day jobs: one runs his own business selling hot dogs in the best-known mall in Skopje, another one owns a small construction company and the third one is a public servant, running social media for the director of Skopje’s state-owned water supply company.
They also run two other websites that aim to churn out as much content as possible, because the more articles they publish, the more the potential revenue from Google Ads.
“We were given sources, mostly Serbian tabloids like Kurir, Informer, Blic and others, and our job was to make the articles seem different than they were [on the newspaper websites] and put clickbait headlines on them,” Karjlievasaid. “We had a quota, like 50 articles in an eight-hour period, but it was so easy.”
In the current media environment in North Macedonia, ‘real’ jobs are almost impossible to find, and producing clickbait content is one of the few options for young journalists, she explained.
“If you are looking for a job in media, it is more likely for a young person like me to choose to work for a website like this one for six hours a day and a 450-to-500-euro fee. Working from home and just doing nothing but copy-pasting and adjusting,” she said.
“The alternative is to find jobs that are not really available in real media like TV stations or NGOs. I said to myself: ‘Why not?’ And these days I can say that many of my peers do not feel this is wrong, they want to be like my owners.”
She said she has seen how easy it can to make money from clickbait sites: “If I had been ambitious about this, I swear to you that in two years from now I could have been running 15 websites like this, employing five people and earning as much as any big-shot, politically-connected Balkan editor-in-chief,” she declared.
It is already hard to attract young people to work in the media in North Macedonia because it’s such a politically-dominated environment, and the rise of the clickbait industry could make the problem worse, experts believe.
Maja Jovanovska, a member of North Macedonia’s Association of Journalists who works on the issue of the lack of young reporters in the country’s media, said that there are more than 100 websites in the country operating on the clickbait model – purely led by Google Ads’ algorithms, with no editorial ethics or standards.
“People’s access to genuine information is being limited,” said Jovanovska. “This is how we influence people’s lives, by giving them poor-quality information.”
Conspiracy theories become profitable
Karatseva left the website two months ago, not long after the owners announced an editorial shift towards political and coronavirus-related news.
“They gave us a list of sources, mostly very questionable sources, from Russia and Serbia, and the US and Croatia as well,” she recalled.
“Domestic news was also included, we were told that we should do news not just about every comment that the minister of health made on live TV or on Twitter or Facebook or in the press, but also even from the comments made about him. That attracts readers, the management said.”
She showed BIRN some of the articles that the site has been publishing recently – some of them praising the authorities’ COVID-19 policies, others condemning them; some of them advocating the idea of protecting oneself from the virus, others pushing conspiracy theories about it.
Indeed, conspiracy theories have become profitable online content in the age of the coronavirus.
Vasko, Meglen, and Vera are all 21-year-old students from Skopje and their job is to translate conspiracy theories from YouTube or other video platforms. BIRN is not naming the company in order to protect their anonymity.
At the company where they work, the employees are divided into two teams: one team of makes transcripts of conspiracy videos from YouTube, while the second team picks up news ideas from the videos and writes short articles or social media posts promoting the conspiracy theory.
“The stories are [about the] ‘deep state’ – anti-liberal, anti-government no matter where, anti-NGO, anti-international institutions like the IMF, the UN, the EU, NATO and, most recently, mostly COVID-does-not-exist conspiracies,” Vasko explained.
He said he found the job four years ago through adverts on LinkedIn and Freelancer.com seeking content writers. Several of his friends, mostly students, also signed up.
“I can earn like $1,500 for like nothing, no brain involved. But I study philosophy and there is a pattern in what we translate. We do not know what the company does this for, but during the COVID-19 crisis I’ve noticed some of the headlines I personally created in some shitty English-language media,” he said.
The company is registered outside North Macedonia and creates clickbait content to order, mostly for right-wing libertarian clients.
“Sorry about this,” he said, “but we’re doing it for the money.”
Saska Cvetkovska is an investigative reporter and media freedom activist. She is a co-founder of Investigative Reporting Lab – Macedonia, an OCCRP member center that fights disinformation with investigative reporting that uses interdisciplinary approaches, including technology and academic research. She serves at the Board of Directors of the Organized Crime and Corruption Reporting project. She was a lead reporter on investigstive project Spooks and Spin — Information Wars in the Balkans, about how Macedonia became a haven for propaganda. Saska has won more than ten domestic and international journalism awards. In 2018 she was elected by Macedonian journalists to represent them on the board of directors of the Association of Journalists of Macedonia, an organization that works to improve working conditions for reporters in the country.
This article has been produced as part of the Resonant Voices Initiative in the EU, funded by the European Union’s Internal Security Fund – Police. The content of this story is the sole responsibility of BIRN. The European Commission does not accept any responsibility for use that may be made of the information it contains.