Not long ago, tuning into a Bulgarian podcast was rare. In just a few years, however, the situation has changed hugely both in terms of choice and listeners’ habits. Productions in different genres increasingly appear out of nowhere, and the podcast format is on the verge of obtaining serious momentum.
Although investigations are still few are far between, the trend has the potential to challenge and diversify Bulgaria’s media landscape, which is clearly problematic; the country was ranked in lowly 111th place in the 2020 World Press Freedom Index, and the overt ties between media outlets, oligarchs and politicians have long drawn unrest and protest.
However, the Bulgarian podcast scene is still in its “punk” phrase, with all its charm and imperfections.
Some of the major local productions are “Govori Internet” (The Internet Speaks), by Elenko Elenkov and Vladimir Petkov-Kaladan, now in its fourth season, which casts an eye on various modern life topics and has a focus on technology; “Ratio”, which delves into science, psychology, politics and tech progress; “Victoria”, by Peter Georgiev, devoted to nerdy bits of football history; “The Urban Detective”, which brings to life little known historical details about Sofia and other major towns; “The Superhuman”, where every episode tells an inspiring story about physical strength, sports, health, and “Falshimento”, which presents new, often under-the-radar music. The bubbling stand-up comedy scene in Sofia meanwhile fuels Comedy Club’s podcast.
Some of the productions that started this year address subjects that are rarely touched upon in great detail in the everyday news cycle and often meet ignorant remarks from the political elite: “Oh Yes”, for example, brings in one four female anchors from various backgrounds and on different locations to discuss feminism, gender issues, sex culture and education; “Girls We Are”, by Bilyana Slaveykova, also focuses on women’s experiences, and this November sees the start of PoliFemme by Katerina Vasileva, which is about women in politics: the debut episode retells the life of the current Belarusian opposition icon Svetlana Tikhanovskaya.
Others explore niche but still important subjects: Stefan Rusinov, a translator from Chinese, just started “Belejka pod linia” (Underline) which is entirely focused on the aspects and challenges of literature translation.
The increasing presence of foreigners living and working in the country in the last decade is also reflected: American Eric D Halsey is documenting local history over the centuries with his popular podcast “The Bulgarian History”, which has now been running for over 120 episodes.
Searching for a depth that’s mssing elsewhere
The Bulgarian branch of the Association of European Journalists recently hosted its first ever “podcast festival”: between November 18 and 22 local and international anchors and journalists discussed the different layers of audio journalism and compared experiences in a Zoom conference, “Power Up: The Power of Podcasting”, which offered public talks and paid workshops.
“The Bulgarian podcast scene is still very young,” Zornitsa Stoilova from Bulgaria’s major weekly newspaper, Capital, said during one of the talks, which is adapting some of its political and business analyses for audio on “The Voice of Capital”. “I hope for more human-centered stories since we’re missing that in our media landscape.”
“The long-form audio is an alternative to clickbait practices. Basically, we’re trying to search for a depth that’s missing elsewhere,” said Elenko Elenkov of “Govori Internet” during one of the panels.
Narrative journalism is also making its way – every episode of “Victoria” delves into different facets of local sport, from the little known history of Bulgaria’s women football to how early 20th century immigrants from Bulgaria created one of the most famous clubs in Uruguay.
“The Urban Detective” is exploring little-researched topics, legends and myths, mainly connected to Sofia: this includes whether The Beatles really almost played in Communist Bulgaria, how far the then regime went in creating an artificial sea near the landlocked capital, or how small-town Yambol was once a vibrant place for countercultural and visionary artists.
“The Urban Detective” has been going for more than two years and is now rounding up its third season. One of its three members, Ana Blagova, says there has been an increasing diversity of content since 2018.
“Also, bigger media outlets are embracing the format which works to make them more recognizable,” Blagova told BIRN. She finds telling stories through audio a more intimate and informal experience than regular journalism. She has substantial experience as a reporter, while her other two colleagues have separate shows on the national broadcaster, Bulgarian National Radio.
Ana finds that audio also benefits the user in a different way, since it takes the listener away from the screen.
“There’s room for a brand new audience, especially today when opening a news website and facing all the bad stories at once is downright overwhelming. I don’t think podcasts can become a full-bodied replacement of everyday journalism but they’re a wonderful companion, a way to enrich your awareness on why a certain topic is important to discuss.
“It also holds a lot of potential in terms of delving into investigating journalism since in a written form you usually present the results; in audio form, the process becomes an ally in engaging the audience,” she observed.
Quantity doesn’t equal quality – yet
Podcast producer Ilyan Ruzhin is cautious about the genre’s rise in the country, however.
“There’s definitely an audience interest, I’d say it’s pretty much an explosion. And it might lead to an implosion soon. I think there’s already more content than what the audience can take, and that’s a result of a wider mediocre content,” he told BIRN.
Ruzhin is behind the long-running music and Patreon-funded podcast “Falshimento”, and part of ProCasters team, a collective that works on recording and producing podcasts in Sofia.
“What’s currently missing are more narrative podcasts; most of the local productions are people who just record their thoughts or make conversations and present them as interviews, without enough of a journalistic integrity.
He adds: “There’s a reason for that void on the scene. Making a podcast is deceptively easy; you just need a mic and a laptop. People often underestimate that you need to use that mic properly, you have to learn how to edit and articulate your speech. So here’s the elephant in the room: what we’re widely lacking are producers, editors, people with proper journalism and storytelling skills involved with the format. All of these boxes should be checked before a production seeks funding.”
However, he is also optimistic that, at some point, quantity will bring quality.
“The really decent Bulgarian podcasts are yet to be recorded. After all, good stories are something that we just naturally stumble upon in Sofia,” he concluded.




 Viktor Orban (C) with Slovenia’s current Prime Minister and leader of the Slovenian Democratic Party, SDS, Janez Jansa (R), and SDS MEP, Milan Zver (R), attending a SDS campaign event in Celje, Slovenia, in May 2018. Photo: EPA
Viktor Orban (C) with Slovenia’s current Prime Minister and leader of the Slovenian Democratic Party, SDS, Janez Jansa (R), and SDS MEP, Milan Zver (R), attending a SDS campaign event in Celje, Slovenia, in May 2018. Photo: EPA
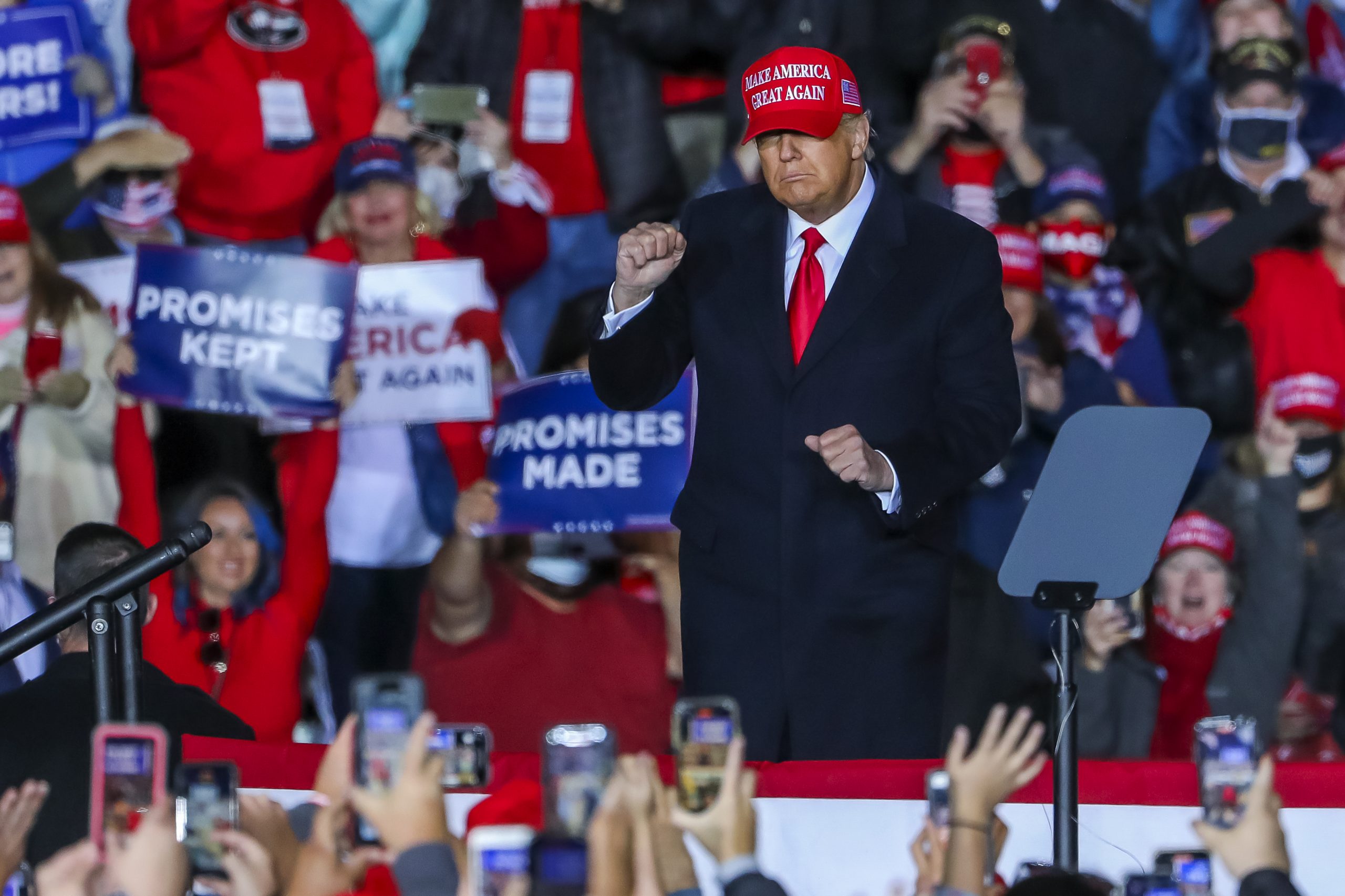








 US President Donald J. Trump participates in a ‘Make America Great Again Victory Rally’ campaign event at the Richard B. Russell Airport in Rome, Georgia, USA, 2020. Photo: EPA-EFE/BRANDEN CAMP
US President Donald J. Trump participates in a ‘Make America Great Again Victory Rally’ campaign event at the Richard B. Russell Airport in Rome, Georgia, USA, 2020. Photo: EPA-EFE/BRANDEN CAMP